The Suspension Bridge
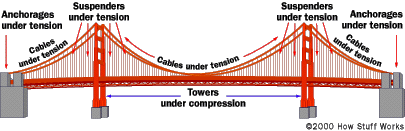
A suspension bridge is one where cables (or
ropes or chains) are strung across the river (or whatever the obstacle happens
to be) and the deck is suspended from these cables. Modern suspension bridges
have two tall towers through which the cables are strung. Thus, the towers are
supporting the majority of the roadway's weight.
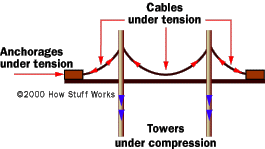
Compression
The force of compression pushes down on the suspension bridge's deck, but
because it is a suspended roadway, the cables transfer the compression to the
towers, which dissipate the compression directly into the earth where they are
firmly entrenched.
Tension
The supporting cables, running between the two anchorages, are the lucky
recipients of the tension forces. The cables are literally stretched from the
weight of the bridge and its traffic as they run from anchorage to anchorage.
The anchorages are also under tension, but since they, like the towers, are
held firmly to the earth, the tension they experience is dissipated.
|
|
|
|
Almost all
suspension bridges have, in addition to the cables, a supporting truss system
beneath the bridge deck (a deck truss).
This helps to stiffen the deck and reduce the tendency of the roadway to sway
and ripple.
�
|
|
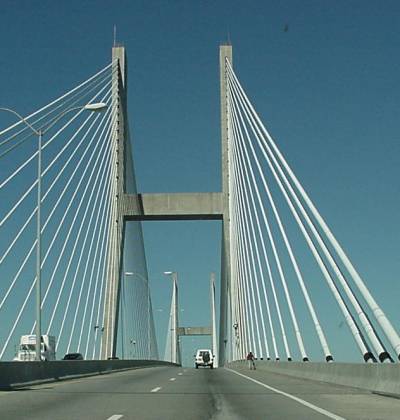
Types of Suspension Bridges
Suspension bridges
come in two different designs: the suspension
bridge, recognized by the elongated 'M' shape, and the less-common cable-stayed design, which has more of
an 'A' shape. The cable-stayed bridge does not require two towers and four
anchorages as does the suspension bridge. Instead, the cables are run from the
roadway up to a single tower where they are secured.
|
|
|
|
|
|
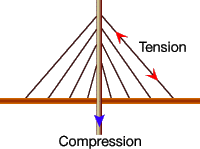
The tower in a
cable-stayed bridge, like its counterpart in a suspension bridge, is responsible
for absorbing and dealing with the compression forces. In both bridges, the
cables are under tension.