The Beam Bridge
A beam bridge is basically a rigid horizontal
structure that is resting on two piers, one at each end. The weight of the
bridge and any traffic on it is directly supported by the piers. The weight is
traveling directly downward.
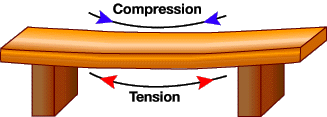
Compression
The force of compression manifests itself on the top side of the beam bridge's
deck (or roadway). This causes the upper portion of the deck to shorten.
Tension
The result of the compression on the upper portion of the deck causes tension
in the lower portion of the deck. This tension causes the lower portion of the
beam to lengthen.
Example
Take a two-by-four and place it on top of two empty milk crates -- you've just
created a crude beam bridge. Now place a 50-pound weight in the middle of it.
Notice how the two-by-four bends. The top side is under compression and the
bottom side is under tension. If you keep adding weight, eventually the
two-by-four will break. Actually, the top side will buckle and the bottom side
will snap.
|
|
Dissipation
Many beam bridges that you find on highway overpasses use concrete or steel
beams to handle the load. The size of the beam, and in particular the height of
the beam, controls the distance that the beam can span. By increasing the
height of the beam, the beam has more material to dissipate the tension. To
create very tall beams, bridge designers add supporting lattice work, or a truss, to the bridge's beam. This
support truss adds rigidity to the existing beam, greatly increasing its
ability to dissipate the compression and tension. Once the beam begins to
compress, the force is dissipated through the truss.
Despite the ingenious
addition of a truss, the beam bridge is still limited in the distance it can
span. As the distance increases, the size of the truss must also increase,
until it reaches a point where the bridge's own weight is so large that the
truss cannot support it.
Types of Beam Bridges
Beam bridges come in dozens of different
styles. The design, location and composition of the truss is what determines
the type. In the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, beam-bridge
construction in the United States was developing rapidly. Designers were coming
up with many different truss designs and compositions. Wooden bridges were
being replaced by all-iron or wood-and-iron combinations. The different truss
patterns also made great strides during this period. One of the most popular
early designs was the Howe truss,
a design patented by William Howe in 1840.
|
|
His innovation came
not in the pattern of his truss, which was similar to the already existing
Kingpost pattern, but in the use of vertical iron supports in addition to
diagonal wooden supports. Many beam bridges today still use the Howe pattern in
their truss.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Truss Strength
A single beam spanning any distance
experiences compression and tension. The very top of the beam experiences the
most compression, and the very bottom of the beam experiences the most tension.
The middle of the beam experiences very little compression or tension.
If the beam were
designed so that there was more material on the top and bottom, and less in the
middle, it would be better able to handle the forces of compression and tension.
(For this reason, I-beams are more rigid than simple rectangular beams.)
A truss system
takes this concept one step further. Think of one side of a truss bridge as a
single beam. The center of the beam is made up of the diagonal members of the
truss, while the top and bottom of the truss represent the top and bottom of
the beam. Looking at a truss in this way, we can see that the top and bottom of
the beam contain more material than its center (corrugated cardboard is very
stiff for this reason).
In addition to the
above-mentioned effect of a truss system, there is another reason why a truss
is more rigid than a single beam: A truss has the ability to dissipate a load
through the truss work. The design of a truss, which is usually a variant of a triangle,
creates both a very rigid structure and one that transfers the load from a
single point to a considerably wider area.